- 12 Jul
- 2023
Ilustrasi gambar (Shutterstock)
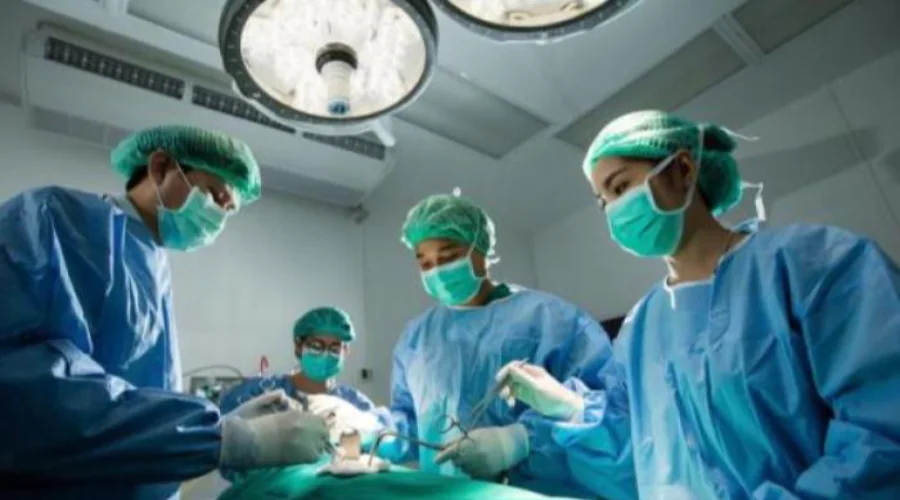
Why should you fast before surgery? This is the Explanation of a UM Surabaya Lecturer
Ordinary people sometimes do not understand the reasons why before surgery, patients must fast first. It is not uncommon for the patient's family to give food or drink without the knowledge of the doctor or nurse because they feel sorry for the patient. Even though of course it is very dangerous for patient safety when the operation is carried out.
When a patient is planned for surgery, they will usually be asked to fast 6-8 hours before the operation is carried out. This is very important to maintain patient safety during surgery, and vice versa if the patient does not fast as recommended before surgery it will be very dangerous for the patient's condition.
In surgical procedures, the patient will be anesthetized or given anesthetic drugs, with the aim that the patient will not feel pain during the operation, and at the same time during some operations the patient will be made unconscious.
Firman, a lecturer at the Faculty of Health Sciences (FIK) UM Surabaya, said that this anesthetic action is closely related to why a patient has to fast. There are several anesthetic techniques that the doctor or anesthesiologist will choose, namely general anesthesia, half-body anesthesia, anesthesia for one area of the body's organs, and local anesthesia.
According to him, the selection of the anesthetic technique will consider several factors, including: the location of the patient's disease for which the operation will be carried out, the history of the patient's illness and of course considering the patient's safety and comfort. All anesthetic procedures for planned operations require sufficient fasting preparation, except for local anesthesia.
General anesthesia is carried out in a way the patient is made completely unconscious, which when the patient is unconscious, will cause loss of cough reflex and swallowing reflex, as well as loss of control of the sphincter or valve in the stomach which regulates the return of stomach contents to the throat.
"Fasting before surgery is intended so that the patient does not vomit, which can cause stomach contents to rise into the throat, then because of the loss of coughing and swallowing reflexes it can cause the patient to choke so that the rest of the vomit will enter the lungs, causing damage to the lungs, resulting in the patient experiencing shortness of breath. breath and severe hypoxia," said Firman Wednesday (12/7/23)
Therefore, before the operation is carried out, the patient is asked to fast so that the patient does not vomit during the operation. So that the operation process can run well.
"After the operation, the patient still has to fast until he is allowed to eat by the doctor or nurse on duty. Usually the patient is allowed to eat when the patient is conscious, with optimal awareness, blood pressure returns to normal, the patient can cough and swallow again," said Firman.








(0) Comments